Signage for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Signage for electric vehicle (EV) charging stations is an important consideration at workplaces, public charging stations, parking garages, and multifamily housing that offer access to EV charging infrastructure. Appropriate charging station signage can:
- Help EV drivers navigate to and identify charging stations
- Optimize use of charging infrastructure by helping all drivers understand that parking spaces at charging stations are for EVs only
- Provide information about policies—such as access, time limits, and hours of use—and facilitate enforcement
- Enable uptake of EVs by providing visibility for charging infrastructure to prospective EV drivers
- Identify charging station corridors.
Signage for charging stations falls into two categories: wayfinding signage and station signage.
Wayfinding Signage for Charging Stations
Wayfinding signage helps EV drivers navigate to charging stations from other locations, such as a freeway exit. The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) defines the minimum standards for signage, which it publishes in the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD), updated every five to six years. The standards in the MUTCD apply to all signage on public highways, streets, bikeways, and private roads open to the public, such as at shopping centers and airports. Wayfinding signage is classified in the MUTCD as either General Service signs or Specific Service signs. Currently General Service signs are allowed by FHWA and the MUTCD for notifying travelers of upcoming services at a highway exit. FHWA has approved the following interim designs for charging station signs:
The eleventh edition of the MUTCD, published December 2023, is the most recent update and includes provisions to ensure adequate flexibility for signage for EV charging infrastructure and Alternative Fuel Corridors. This edition includes the following General Service and Specific Service signs related to EV charging:
General Information Signs, Alternative Fuels Corridors Signs (Chapter 2H, Section 2H.14)

D9-17a (example)
General Service Signs (Chapter 2I)

D9-11bp

D9-11b
Specific Service Signs (Chapter 2J)
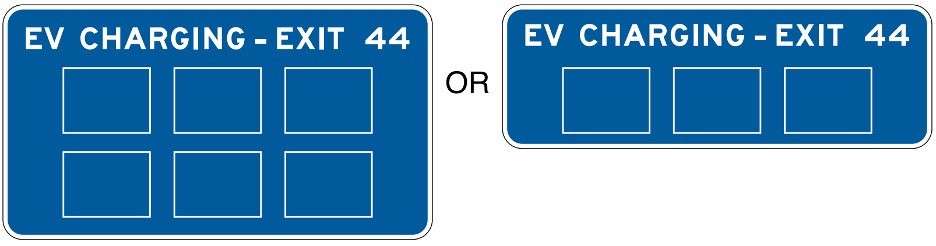
Business Identification Panel Arrangements on Specific Service Signs

D9-17a (example)
For wayfinding purposes, these designs can be combined with directional arrows and mileage. FHWA refers to the signs above as D9-11bp (written description) and D9-11b (symbol). State and local transportation departments may create and add custom signage but they must meet the minimum requirements defined in the MUTCD to help drivers recognize signs from one jurisdiction to the next. General information about sign placement and visibility can be found in Chapter 2A, Part 2 of the MUTCD.
Station Signage
Station signage helps EV drivers identify charging stations. It also helps charging station hosts communicate and enforce policies related to the use of the charging infrastructure and associated parking spaces. For example, a station host may decide that spaces associated with charging stations are only for EVs that are actively charging, or it may decide to place a limit on the amount of time a vehicle may occupy a charging space.

To be enforceable, any signs posted in a public right of way must be supported by local ordinances that specify time limits, penalties, and definitions. Any signs posted in the public right of way must meet MUTCD requirements. Private parking areas that are not open to the public (such as employee parking areas at workplaces or at multifamily housing) are not required to meet MUTCD signage requirements. But organizations that provide charging in private areas may find that consistency with the standards helps all drivers understand and recognize charging station signage.
Pavement markings, painted on the surface of a parking space, can be used to reinforce signage for charging stations. Notably, most jurisdictions deem pavement markings unenforceable on their own. For general information about pavement markings, see Chapter 3B of the MUTCD.
More Information
The California Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (2014 CA MUTCD) includes charging station signage designs and optional pavement markings, as well as policies on traffic control devices. These clarifications can help guide other states interested in adopting more alternative fuel signage. Learn more about California’s standards for charging station signage and pavement markings.
The Minnesota Department of Transportation (MnDOT) also developed a charging infrastructure and siting toolkit for EV chargers at MnDOT facilities, “Electric Vehicle Guidance.” This guide provides information for facilities staff about EVs and general guidance for installing EV charging stations.